2. Supermarine Spitfire
3. Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird
4. Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor
5. Messerschmitt Bf 109
6. Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 Fishbed
7. Boeing B-52 Stratofortress
8. McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II
9. General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon
10. Republic Fairchild A-10 Thunderbolt II Warthog
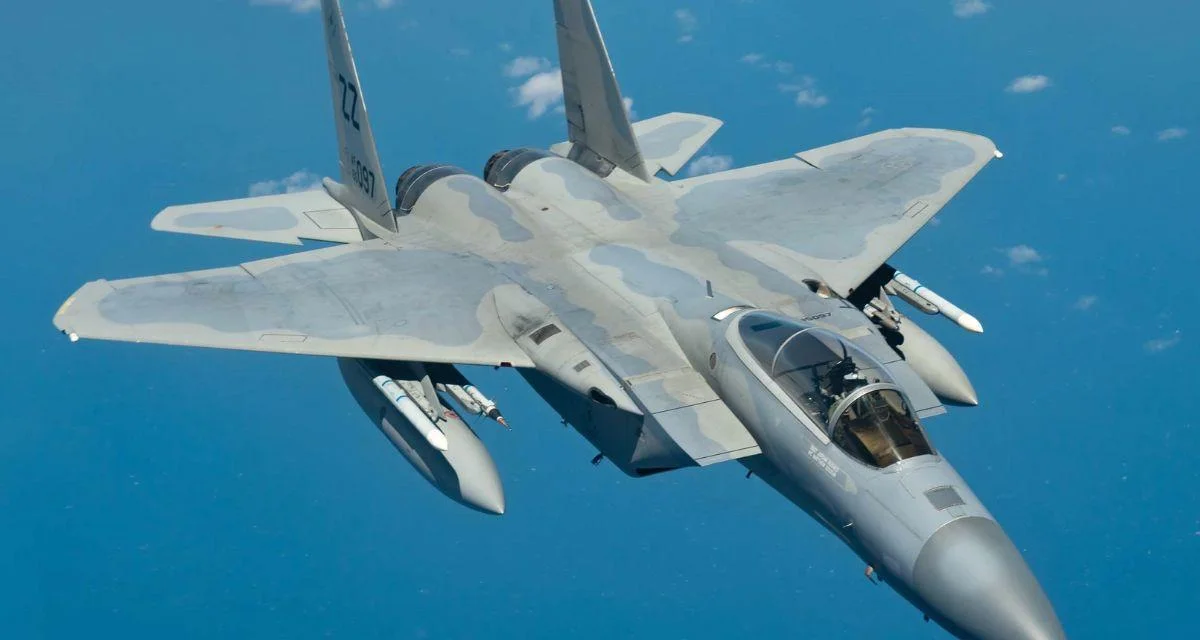
The F-15 Eagle was highlighted for its record of over 100 aerial victories without a single combat loss since entering service in 1972. The article notes that "the Eagle has accumulated over 100 aerial victories since it entered service, with zero combat losses." This was cited as a primary reason for its top ranking.
The Supermarine Spitfire was recognized for its role in the Battle of Britain and its significant production numbers during World War II: "Over 22,000 Spitfires were made before it was finally discontinued, and it claimed over 6,000 aerial victories over the course of WWII in all theaters."
In third place is the SR-71 Blackbird, which remains the fastest jet ever built and served various agencies including the CIA and NASA until its retirement in 1999.
The Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor was described as "the world’s first fifth-generation stealth fighter," noted for having never been lost in combat but also having fewer opportunities due to its limited use.
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 was listed as "the most numerous fighter type made to date," with almost 34,000 built during World War II.
Other notable entries include the MiG-21 Fishbed—recognized as "the most mass-produced supersonic airplane (and any other kind of jet) in history"—and bombers like the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress that has been operational since 1952.
Rounding out the list were multi-role fighters such as the F-4 Phantom II and F-16 Fighting Falcon—both widely produced—and ground attack aircraft like the A-10 Thunderbolt II Warthog.
The article discusses how some omissions from ChatGPT’s list may be surprising given their reputation or impact on military aviation history but highlights that AI-generated rankings can differ from traditional assessments due to algorithmic logic rather than consensus opinion.
 Alerts Sign-up
Alerts Sign-up