Regarding bombers, this remains solely within the Air Force’s domain with a fleet of 140 aircraft. Both services are developing sixth-generation fighters: the Air Force's F-47 focuses on air superiority and long-range strike missions with advanced engines and modular weapons bays; the Navy's F/A-XX is designed for carrier operations with features such as cooperative drone control and networked defenses.
Helicopters serve distinct roles in each branch. The Air Force uses rotorcraft mainly for specialized tasks such as search and rescue or special operations infiltration. It operates about 50 V-22 Ospreys that can reach distant targets inaccessible to traditional helicopters. The Navy relies heavily on rotary-wing aircraft like the CMV-22B Osprey for carrier delivery and Sikorsky SH-60R/S helicopters for antisubmarine missions. On average days, over 100 Air Force rotorcraft are ready compared to nearly four hundred in Navy service.
Both branches maintain intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR), and command-and-control platforms but employ them differently due to their unique mission requirements. The Air Force is transitioning from its aging E-3 Sentry AWACS fleet to modern E-7A Wedgetails while retiring other platforms like the E-8C JSTARS in favor of new technologies such as radar pods and unmanned systems.
For maritime patrols and signals intelligence, Navy assets include platforms like EP-3E Aries II and P-8A Poseidon—an aircraft derived from Boeing’s commercial line that replaced older turboprop models for broad-area surveillance and anti-submarine warfare duties.
Strategic airlift largely falls under Air Force responsibility with heavy transports such as C-17A Globemaster III and C-5M Galaxy moving large equipment globally. Tactical lift comes from C-130s capable of landing on unprepared surfaces. Tanker support is provided by KC-series refuelers that are expected to remain vital components into the next decade.
Navy fixed-wing transport includes short-range C-40A Clippers operating between bases while vertical delivery is handled by CMV-22B Ospreys reaching ships at sea. Marines also operate KC-130Js for cargo transport or refueling missions supporting both logistics and combat operations.
Unmanned aerial systems are becoming increasingly important in both services but follow divergent paths due to different doctrines and operational constraints. The Air Force’s MQ-series Reapers have been central in recent conflicts thanks to their endurance and precision strike capabilities. The Navy’s approach led to development of MQ-25A Stingray drones focused primarily on aerial refueling from carriers.
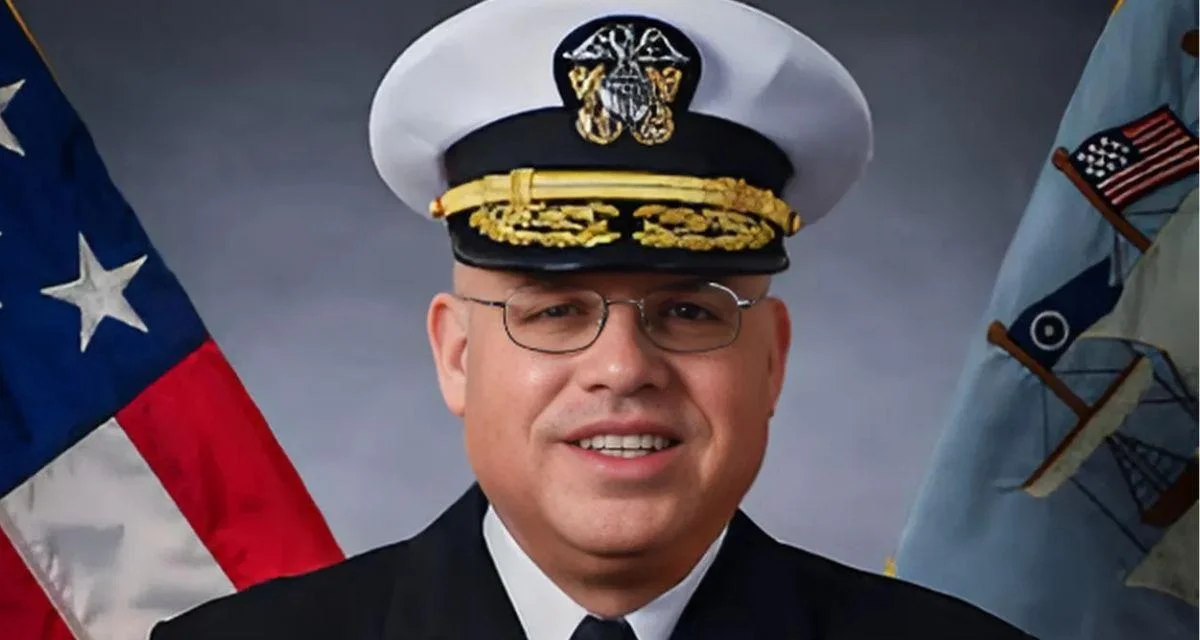
Rear Admiral Michael Mattis highlighted ongoing efforts integrating unmanned systems during his remarks at a Center for Strategic and International Studies event in February 2025: “We’re never going to get to [full integration] through ‘experimentation’ [with robotic unmanned systems without seeing them battle-tested]. We need to figure out how we can use our advanced systems, especially when uncrewed systems become more autonomous [in combat]. It’s not going to be a static fight going forward. [The conflict] shows that a nation with no navy [can stop] one of the world’s premier navies."
While both branches continue experiments—such as "attritable" drones in the Air Force—their approaches reflect fundamental differences shaped by their respective missions at sea or over land.
 Alerts Sign-up
Alerts Sign-up